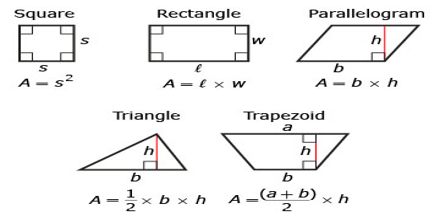
- Basic Area Formulas Pdf
- Basic Area Volume Formulas
- Basic Shape Area Formulas
- Basic Formulas For Areas And Perimeters
- Basic Area Formulas
An alternative to memorizing the 'formula' is just to stop and think about arc circumferences and arc areas logically. You know the formulas for the area and circumference of a circle (because they are in your given equation box on the test). You know how many degrees are in a circle (because it is in your given equation box on the text). Area: Trapezoid Cone Circumference: or ˘ Area: Circle ˘ Perimeter: Area: Parallelogram Cylinder Volume: ˇ Surface Area: ˆ Square or Rectangle Pyramid Volume: ˇ ˙ Rectangular Prism (Box) Volume: ˇ Surface Area: ˆ Cube Volume: ˇ ˙ Surface Area: ˆ ˝ Sphere.
Formula
Pressure, Force and Horsepower Relationships:
Pressure (psi) = force (lbs) / area (in²)
Force (lbs) = area (in²) x pressure (psi)
Area (in²) = force (lbs) / pressure (psi)
Fluid Power Horsepower:
Fluid Power Horsepower (hp) = pressure (psi) x pump flow (gpm) / 1,714
Torque and Horsepower Relationships:
Torque (ft lbs) = horsepower (hp) x 5,252 / speed (rpm)
Horsepower (hp) = torque (ft lbs) x speed (rpm) / 5,252
Speed (rpm) = horsepower (hp) x 5,252 / torque (ft lbs)
Basic Cylinder Calculations:
Piston Cylinder Area (in²) = diameter squared x .7854
(Can also use 3.1416 x radius squared (ins) )
Piston Rod End (annulus end) Area (in²) = piston cylinder area (in²) - rod area (in²)

Cylinder Force (lbs) = pressure (psi) x area (in²)
Cylinder Speed (ft/min) = 19.25 x flow rate (gpm) / area (in²)
(Divide by 60 to convert speed to ft/sec)
Cylinder Speed (in/min) = flow rate (cu ins/min) / area (in²)
(Note that 1 US gallon = 231 cu ins)
Cylinder Time (secs) = area (in²) x cylinder stroke (ins) x .26 / flow rate (gpm)
Cylinder Flow Rate (gpm) = 12 x 60 x cylinder speed (ft/sec) x area (in²) / 231
Cylinder Volume Capacity (gals) = cylinder area (in²) x cylinder stroke (ins) / 231
Basic Hydraulic Motor Calculations:
Motor Torque (in lbs) = pressure (psi) x motor displacement (cu ins/rev) / 6.28
(Can also use horsepower (hp) x 63,025 / speed (rpm)
Motor Speed (rpm) = 231 x flow rate (gpm) / motor displacement (cu ins/rev)
Motor Horsepower (hp) = torque (in lbs) x motor speed (rpm) / 63,025
Motor Flow Rate (gpm) = motor speed (rpm) x motor displacement (cu ins/rev) / 231
Motor Displacement (cu ins/rev) = torque (in lbs) x 6.28 / pressure (psi)
Basic Pump Calculations:
Pump Outlet Flow (gpm) = pump speed (rpm) x pump displacement (cu ins/rev) / 231
Pump Speed (rpm) = 231 x pump flow rate (gpm) / pump displacement (cu ins/rev)
Pump Horsepower (hp) = flow rate (gpm) x pressure (psi) / 1,714 x pump efficiency factor
(Can also use horsepower (hp) = torque (in lbs) x pump speed (rpm) / 63,025)
Pump Torque (in lbs) = pressure (psi) x pump displacement (cu ins/rev) / 6.28
(Can also use horsepower (hp) x 63,025 / pump displacement (cu ins/rev)
Heat Generation Formulas: Converting heat into other units
1 hp = 2,545 BTU/hr = 42.4 BTU/min = 33,000 ft. lbs./min = 746 watts
Horsepower (hp) = pressure (psi) x flow (gpm) / 1714 -or- BTU/hr = 1½ x psi x gpm
1 BTU/hr = .0167 BTU/min = .00039 hp
Example: 10 gpm flow across a pressure reducing valve with a 300 psi drop = 1.75 hp of heat generated
1.75 hp of heat = 4,453 BTU/hr = 105 BTU/min = 57,750 ft. lbs./min = 1,305 watts
- Most of this heat will be carried back to the reservoir.
- Note that heat is generated anytime no mechanical output work is produced
General cooling capacity of a steel reservoir: HP (heat) = .001 x TD x A
TD = temperature difference of the oil in the reservoir and the surrounding ambient air
A = entire surface area of the reservoir in square feet (including the bottom if elevated)
General Information and “Rules of Thumb”:
Estimating pump drive horsepower: 1 hp of input drive for each 1 gpm at 1,500 psi pump output
Horsepower when idling a pump: an idle and unloaded pump will require about 5% of its full rate hp
Reservoir capacity (GALS) = length (INS) x width (INS) x height (INS) / 231
Oil compressibility: 1/2 % approximate volume reduction for every 1,000 psi of pressure
Water compressibility: 1/3 % approximate volume reduction for every 1,000 psi of pressure
Wattage to heat hydraulic oil: each 1 watt will raise the temperature of 1 gallon of oil by 1°F per hour
Guidelines for flow velocity in hydraulic lines:
- 2 to 4 ft/sec = suction lines
- 10 to 15 ft/sec = pressure lines up to 500 psi
- 15 to 20 ft/sec = pressure lines 500 – 3,000 psi
- 25 ft/sec = pressure lines over 3,000 psi
- 4 ft/sec = any oil lines in air-over-oil systems
Velocity of oil flow in a pipe: velocity (ft/sec) = flow (gpm) x .3208 / inside area of the pipe (sq ins)
Circle area formulas:
- Area (sq ins) = π x r² where π (pi) = 3.1416 and r = radius in inches squared
- Area (sq ins) = π x d² / 4 where π (pi) = 3.1416 and d = diameter in inches
- Circumference (ins) = 2 x π x r where π (pi) = 3.1416 and r is radius in inches
- Circumference (ins) = π x d where π (pi) = 3.1416 and d = diameter in inches

Basic Area Formulas Pdf

Commonly Used Fluid Power Equivalents:
One US gallon equals:
- 231 cubic inches
- 3.785 liters (1 liter = .2642 US gals)
- 4 quarts or 8 pints
- 128 ounces liquid / 133.37 ounces weight
- 8.3356 pounds weight
One horsepower equals:
Basic Area Volume Formulas
- 33,000 ft lbs per minute
- 550 ft lbs per sec
- 42.4 BTU per min
- 2,545 BTU per hour
- 746 watts
- 0.746 kw
On psi equals:
Basic Shape Area Formulas
- .0689 bar (1 bar = 14.504 psi)
- 6.895 kilopascal
- 2.0416 hg (inches of mercury)
- 27.71” water
One atmosphere equals:
Basic Formulas For Areas And Perimeters
- 14.696 psi
- 1.013 bar
- 29.921 hg (inches of mercury)
Basic Area Formulas
Note: This information is provided as a quick reference resource and is not intended to serve as a substitute for qualified engineering assistance. While every effort has been made to ensure the accuracy of this information, errors can occur. As such, neither Flodraulic, any of its affiliated companies nor its employees will assume any liability for damage, injury or misapplication as result of using this reference guide.
